- All materials are made up of atoms;
- These atoms contribute to the electrical properties of a material, including its ability to conduct electrical current;
- For purposes of discussing electrical properties, an atom can be represented by the valence shell and a core that consists of all the inner shells and the nucleus;
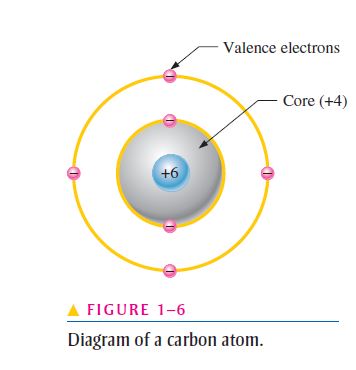
- This concept is illustrated in Figure 1–6 for a carbon atom;
- Carbon is used in some types of electrical resistors;
- Notice that the carbon atom has four electrons in the valence shell and two electrons in the inner shell;
- The nucleus consists of six protons and six neutrons, so the 6 indicates the positive charge of the six protons;
- The core has a net charge of 4 (6 for the nucleus and for the two inner-shell electrons);
Insulators
- An insulator is a material that does not conduct electrical current under normal conditions;
- Most good insulators are compounds rather than single-element materials and have very high resistivities;
- Valence electrons are tightly bound to the atoms;
- Therefore, there are very few free electrons in an insulator;
- Examples of insulators are rubber, plastics, glass, mica, and quartz;
Conductors
- A conductor is a material that easily conducts electrical current;
- Most metals are good conductors;
- The best conductors are single-element materials, such as copper (Cu), silver (Ag), gold (Au), and aluminum (Al), which are characterized by atoms with only one valence electron very loosely bound to the atom;
- These loosely bound valence electrons become free electrons. Therefore, in a conductive material the free electrons are valence electrons;
Semi-Conductors
- A semiconductor is a material that is between conductors and insulators in its ability to conduct electrical current;
- A semiconductor in its pure (intrinsic) state is neither a good conductor nor a good insulator;
- Single-element semiconductors are antimony (Sb), arsenic (As), astatine (At), boron (B), polonium (Po), tellurium (Te), silicon (Si), and germanium (Ge);
- Compound semiconductors such as gallium arsenide, indium phosphide, gallium nitride, silicon carbide, and silicon germanium are also commonly used;
- The single-element semiconductors are characterized by atoms with four valence electrons;
- Silicon is the most commonly used semiconductor;