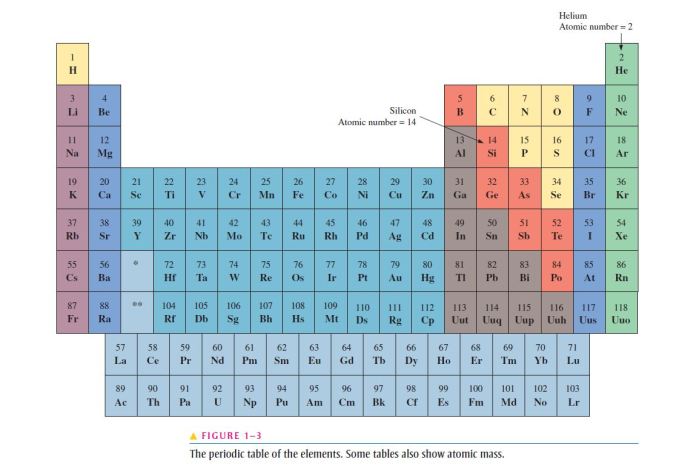
- All elements are arranged in the periodic table of the elements in order according to their atomic number;
- The atomic number equals the number of protons in the nucleus, which is the same as the number of electrons in an electrically balanced (neutral) atom;
- For example, hydrogen has an atomic number of 1 and helium has an atomic number of 2;
- In their normal (or neutral) state, all atoms of a given element have the same number of electrons as protons;
- The positive charges cancel the negative charges, and the atom has a net charge of zero;
- Atomic numbers of all the elements are shown on the periodic table of the elements in Figure 1–3;